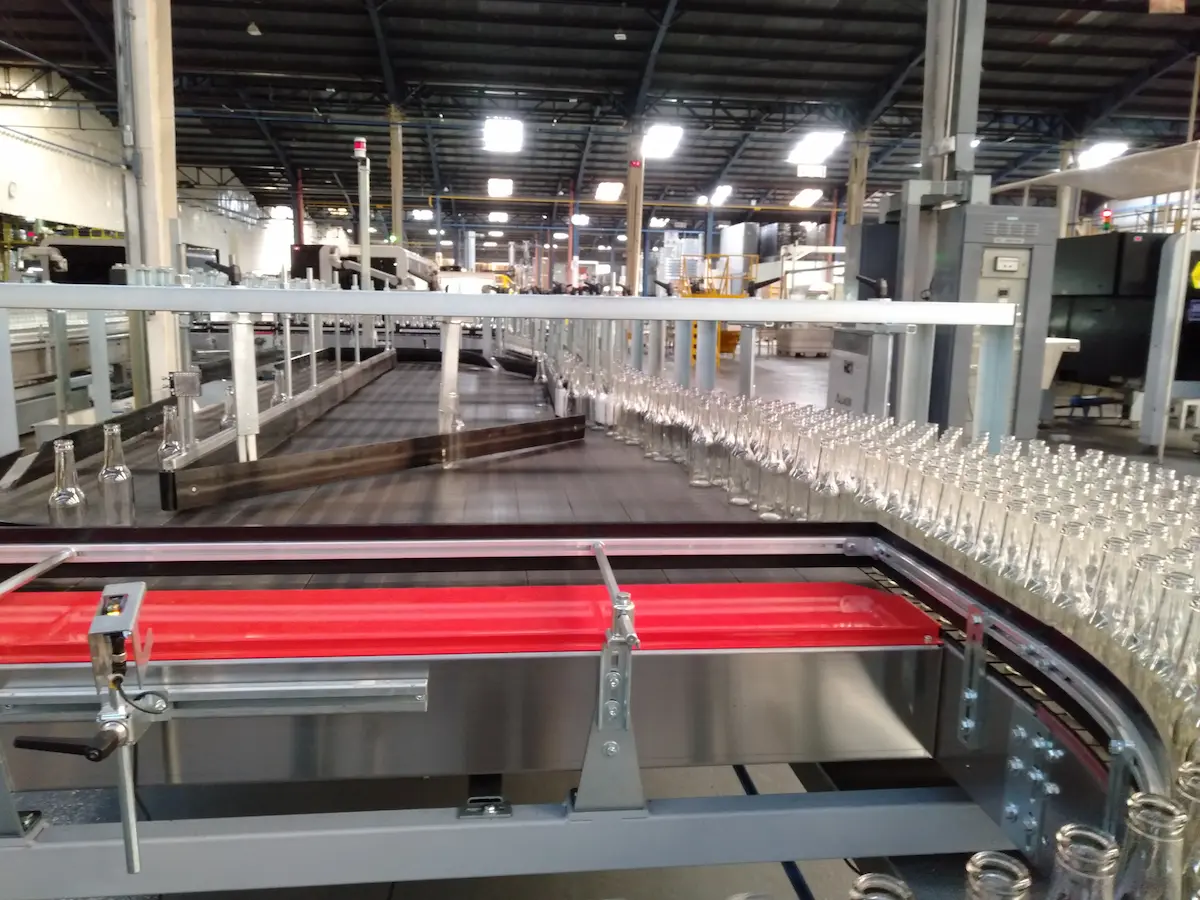
In the industrial sector, terms like assembly plant and production plant may seem similar, but these facilities serve distinct purposes. This article explains these differences, clarifying the unique roles each type of plant plays in creating a finished product.
What is an Assembly Plant?
An assembly plant is responsible for putting together pre-manufactured parts to create a final, operational product. Often used in packaging or filling lines, this facility takes various components and assembles them into a product ready for distribution.
What is a Production Plant?
Unlike an assembly plant, a production plant manages the entire transformation of raw materials into a finished product. This process includes various stages, from raw material processing to creating consumer-ready items.
Key Differences Between Production and Assembly
- Production: This phase involves working with raw materials to obtain a consumable product.
- Assembly: This phase focuses on assembling all necessary components, allowing the product to be used or sold.
Who Runs Manufacturing Plants?
Typically, manufacturing plants are managed by company owners or operational managers responsible for overseeing the plant’s productivity and efficiency.
Examples of Assembly and Production Plants
A common example of a production plant is a tomato processing factory, where tomatoes are transformed into consumable products like sauces or canned tomatoes. An example of an assembly plant is a facility where parts are put together to form a complete machine.
What is Considered a Manufacturing Plant?
A manufacturing plant generally refers to any facility dedicated to transforming or packaging products. These can include both production and assembly plants, each contributing essential roles in different stages of production.
For more info, contact us to discover how we work!
